Roland Berger advises the aerospace, defense and security industries. We support OEMs, suppliers, agencies and investors.


Space-enabled Germany
Why space is crucial to Germany's economic competitiveness, sovereignty, and sustainability goals
The space industry and the space-enabled solutions it offers have the potential of boosting Germany’s innovative capabilities and international competitiveness, helping the country navigate the challenges of geopolitical shifts and macroeconomic complexity.

"The benefits of a vibrant space economy are obvious. Governments and industry need to work hand in hand to create a future where the sky is not a limit, but a gateway to limitless opportunities."
In an era marked by extraordinary challenges and remarkable opportunities, the German economy faces a complex economic landscape. As it strives for greater competitiveness, innovation, resilience, and sustainability, the space sector holds the potential to serve as a convergence point for addressing these challenges.
The space economy's value chain can be segmented into the upstream and downstream sectors. Upstream activities includes the production of launchers and satellites while the downstream generates "space-enabled solutions" that enhance existing industries, create new markets, and ensure the independence and resilience of our infrastructures and societies.
In addition to these two streams, the space sector generates wider benefits for the society, such as spillovers from space technologies, improved global trade, and better access to healthcare. Today’s space-enabled solutions areas are predominantly derived from Positioning, Navigation & Timing (PNT), Earth Observation (EO), Meteorology, and Satellite Communication. Many other applications such as space-based solar power are not yet market ready or have yet to be invented.
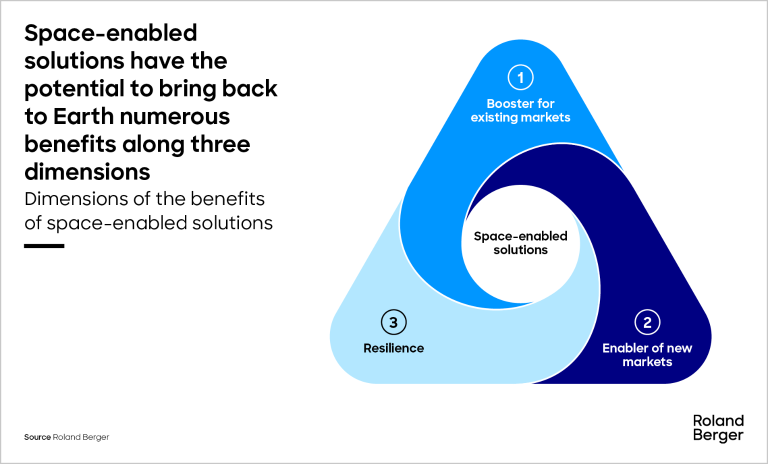
Even with the space-enabled solutions available today, the space industry has a significant impact on modern society and the economy in various ways, contributing notably to economic progress on a global scale. Space-enabled solutions can be grouped into three types of benefits they bring:
Firstly, space-enabled applications serve as boosters for existing business models in traditional industries. For example, they can improve logistical routes by coupling meteorological data and positioning data to enhance maritime transport.
Furthermore, space-enabled solutions serve as enablers for entering new markets and business domains. For instance, with global satellite coverage for broadband and IoT, and high-precision navigation via satellite, new businesses associated with the automotive sector – a strategic sector for Germany – can be enabled (e.g., a permanent link to satellites for software-defined vehicles, Vehicle-to-Infrastructure business models).
Finally, a space infrastructure offering global connectivity guarantees resiliency in our increasingly digitalized and connected economies. While terrestrial internet is highly susceptible to disruptions caused by human or natural factors, satellite internet provides an alternative backup. As the costs of operating satellite constellations have consistently decreased in recent years, the costs of internet outages are significantly increasing. Today, a hypothetical nationwide one-day internet outage in Germany would cause an economic loss of approximately EUR 1.4 bn.
Space-enabled solutions: a EUR 1 trillion+ potential in 2040
Space-enabled solutions offer significant economic advantages to various sectors, acting as a strong booster for organizations capable of leveraging such technologies to gain a competitive edge. Roland Berger has developed a model that predicts the anticipated demand for space-enabled applications spanning Earth Observation and PNT in 17 distinct industrial sectors. Furthermore, it takes into account the overall future expansion of the SatCom market. This model offers valuable insights into the prospective market size of space-enabled solutions. These solutions have applications across various sectors, encompassing autonomous driving (automotive), precision farming (agriculture), telemedicine (healthcare), as well as the enhancement of wind farms and solar power plants.
According to our forecast, space-enabled solutions are projected to represent approximately EUR 1.25 trillion by 2040. This growth will be driven by increasing digitalization and dependence on communication infrastructure, including space-based technologies. The automotive sector is expected to experience significant growth, with cars requiring hardware and software solutions for positioning and communication. This is essential due to the rising data exchange between vehicles and the surrounding infrastructure. In Germany, the automotive industry stands to gain from a thriving European space-enabled economy.
Additionally, in the consumer sector, the growing connectivity of devices like smartphones and wearables, equipped with positioning chips, will meet the rising demand for location-based apps, such as ridesharing and fitness apps. Other sectors, such as energy, logistics, and agriculture, will also witness increased adoption of space-enabled solutions.
Will Germany miss out on the opportunities of being a space-enabled nation?
Significant developments have unfolded in the space sector since the early 2000s, with a progressive transformation marked by the increasing involvement of private companies. The United States have notably thrived due to this sectoral shift, leveraging new capabilities in space transportation and global communication via satellites, driven by strong national ambitions from both public and private entities. In this global competition, China is rapidly increasing its investments, while other nations are launching their own initiatives in the space sector, leading to the creation of more space agencies (such as the UAE in 2014, New Zealand in 2016, and Spain in 2023).
In sharp contrast, Germany is contemplating reductions in its space budget and trails behind other space-faring nations in both public funding and private investments. The question remains: will Germany seize the opportunity or risk being left behind in the evolving landscape of space-enabled economies?
In addition to the reduced funding volume, we have identified four challenges that hinder Germany from becoming a "space-enabled economy." Firstly, there is a lack of awareness among a significant portion of society, as well as among key decision-makers in business and politics, regarding the potential that space-based applications offer for the industry. Secondly, there is currently a lack of tailored solutions specifically designed to meet the needs of individual industries. These targeted applications are crucial to promote the broad acceptance and use of space technologies in various economic sectors.
Furthermore, the availability of qualified professionals presents a challenge, particularly for companies within the space industry. Finally, there is a need for political ambitions regarding sovereignty in space. A clear commitment to these ambitions is crucial for establishing space-enabled solutions in various industries in the long term.
To stay competitive with other space nations, Germany doesn't need to reinvent the wheel. Studying best practices from partner countries like the US. Germany could pave the path toward wider private sector integration of space-enabled solutions by initially promoting public institutions to adopt these technologies. Through sustained public demand established by anchor tenant contracts, providers of space-enabled solutions can expand their operations and drive down costs, ultimately making these innovations accessible to a broader audience. Valuable insights from other countries also underscore the importance of establishing and leveraging public-private partnerships for the purpose of promoting providers of space-enabled services.
Many foundations have been laid in Germany; now it's time to leverage these and guide developments in Germany. Space sovereignty is crucial for fully benefiting from space-enabled solutions in the industrial sector.
Register now to access the full study, that explores why the space industry is crucial to Germany in many different areas. Additionally, you get regular news and insights.


![Roland Berger forecasts of the space-enabled solutions market [EUR bn]](https://img.rolandberger.com/content_assets/content_images/captions/Roland_Berger_INS_1162_New_space_with_BDI_GT02_new_image_caption_none.png)
![Private investments in space companies offering space-enabled solutions [# deals and volume in EUR bn, cumulative 2013 - 2022]](https://img.rolandberger.com/content_assets/content_images/captions/Roland_Berger_INS_1162_New_space_with_BDI_GT03_image_caption_none.png)
