Why Space is crucial to Germany's economic competitiveness, sovereignty, and sustainability goals...


Space enabled KSA
The space sector holds immense potential for the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia (KSA), offering a pathway to position the country as a regional leader, showcase its technological capabilities, and advance its Vision 2030 objectives. Space exploration can bring many benefits across various critical sectors, all vital to the Kingdom's future. This article explores the intersection of KSA's strategic ambitions and the untapped opportunities of space-enabled solutions.

The discussion centers on select use cases that illustrate how space technologies can be harnessed to drive progress in the post-oil era, enhance the well-being of citizens, and address defense and security needs. However, realizing these ambitions is not a solitary endeavor. The complexity and scale of the space sector necessitate a comprehensive ecosystem to support it, one that thrives on collaboration among government agencies, private enterprises, academic institutions, and international partners. This collaborative foundation is beneficial and crucial for sustainable growth and success in space endeavors.
What are space-enabled solutions?
The space economy is experiencing an unparalleled surge of interest, evident in the expanding constellation of satellites orbiting Earth, substantial investments from both public and private sectors, and the emergence of groundbreaking applications leveraging satellite data. Numerous countries and commercial enterprises pour resources into space programs, underscoring a global acknowledgment of space exploration and technology's vast opportunities and advantages for scientific advancement, economic prosperity, and national security.
Leveraging space-derived data for the betterment of our planet.
As Roland Berger’s article on space-enabled solutions elaborates, the space economy's value chain can be segmented into the upstream and downstream sectors. Upstream activities involve producing launchers and satellites, while the downstream sector creates 'space-enabled solutions' that enhance existing industries and open new markets ensuring infrastructure, societal independence, and resilience. This potential for growth and innovation makes the space sector exciting and full of opportunity.
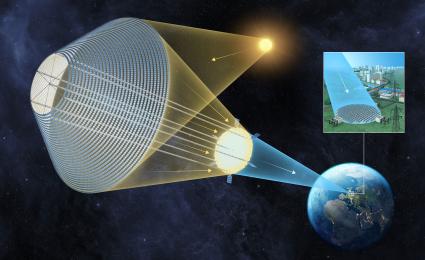
The space sector brings about various benefits for society and its two main streams. These benefits include spillovers from space technologies, enhanced global trade through navigation services, and improved access to healthcare through telemedicine. The current focus of space-enabled solutions revolves around Positioning, Navigation & Timing (PNT), Earth Observation (EO), Meteorology, and Satellite Communication. Although many other applications, such as space-based solar power, are not yet market-ready or have yet to be invented.
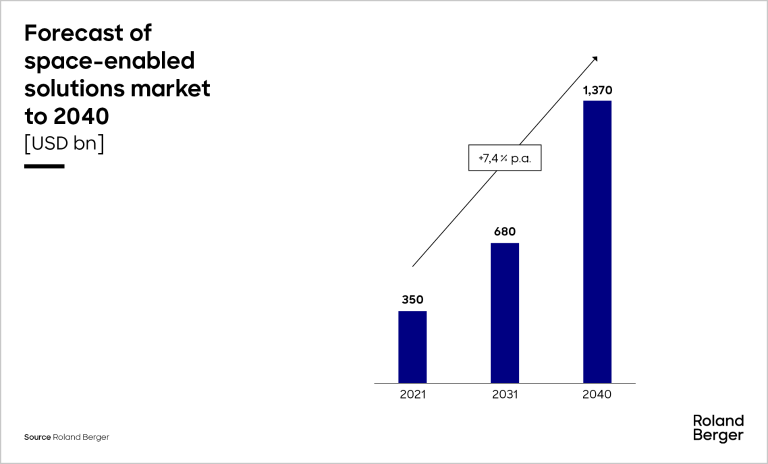
Space-enabled solutions: a USD 1 trillion+ potential in 2040
Space-enabled solutions provide significant economic advantages to various sectors and act as a potent booster for organizations that can leverage such technologies to gain a competitive edge. Roland Berger has developed a model that predicts the anticipated demand for space-enabled applications, including Earth Observation and PNT, in 17 distinct industrial sectors. The model also considers the overall future expansion of the SatCom market. This model offers valuable insights into the prospective market size of space-enabled solutions, which have applications across various sectors such as autonomous driving (automotive), real estate monitoring (urban development), tourism, and the enhancement of oil & gas and renewable energy plants.
According to our forecast, space-enabled solutions are projected to represent approximately USD 1.37 trillion by 2040. Four main factors will drive this growth:
- Reduced cost of deploying satellites, driven by advancements in reusable rocket technology and increased competition in the space launch industry
- Improved space accessibility as entrepreneurs, startups, and academia establish their satellite fleets
- Greater utilization of satellite signals for enhanced connectivity, data-driven decision-making, and innovative solutions, fueling the growth of new applications and business models
- Increased proliferation of smart and connected devices and greater demand for seamless global connectivity
Why should KSA invest in space?
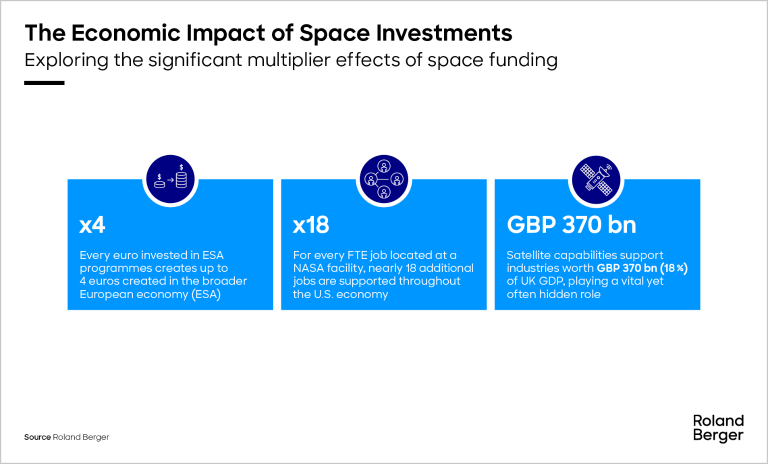
The space sector presents a compelling case for investment, yielding favorable impacts on GDP and employment creation while delivering substantial cross-sector benefits. In addition to its direct economic contributions, the space industry profoundly influences the overall economy, with its effect further magnified through indirect and induced repercussions. Furthermore, space showcases a nation's technological leadership, significantly bolstering its global standing, attracting foreign investments, and shaping international perceptions. Indirectly, the space sector spurs demand for suppliers, while induced impacts stem from the expenditure of space industry personnel, amplifying its economic footprint.
The impact of the space economy exceeds its quantifiable economic implications. Space technologies have become deeply integrated into the operations of diverse industries such as agriculture, transport and logistics, mining and quarrying, forestry and fishing, construction, and energy. Space-based infrastructure is increasingly indispensable for supporting critical societal functions, including telecommunications, finance, and utilities.
Non-space sectors primarily benefit from space investments through cost savings and avoidance (e.g., in comparison to terrestrial solutions).
Space as an enabler for KSA’s Vision 2030
As KSA progresses towards achieving its goals outlined in Vision 2030, exploring space has emerged as a powerful driver for growth across all pillars of the vision. It is a significant facilitator, substantially enhancing the nation's industrial capabilities and competitive edge.
Investing in the space sector can diversify the economy by creating new industries, generating employment opportunities, and attracting investments. Space programs also drive innovation and technological advancement, nurturing an environment of research and development that can extend into other sectors of the economy, propelling growth and competitiveness. Most importantly, space exploration can inspire the next generation of scientists, engineers, and innovators, fostering a culture of curiosity, exploration, and lifelong learning.
What is the potential for space in KSA?
The KSA space industry is anticipated to experience significant growth in the coming years. The average annual market value is projected to rise from an estimated USD 1.2 billion per year (based on the average from 2015 to 2022) to between USD 2.1 billion and USD 3.5 billion per year (estimated average from 2023 to 2030). This market expansion is closely tied to KSA's ambitious plans to develop new space programs and its commitment to maximizing the localization of related activities.
KSA has already made substantial investments in the Space sector as part of its broader economic diversification and development strategy, with USD 2.1 bn earmarked for investment in the space program by 2030. These investments in space technology underscore the Kingdom's aspirations to position itself as a global space exploration and innovation leader while simultaneously fostering domestic talent and job creation in cutting-edge industries.
There have been many notable investments in space, such as PIF’s USD 270 million investment in the HK Aerospace Technology group to establish a satellite manufacturing facility in the Kingdom.
However, the downstream space sector is anticipated to take precedence in the coming years, accounting for over 50% of the average annual market value in 2023-2030. This underscores the importance of timely and strategic identification of potential opportunities, all aligning closely with KSA's national goals and strategic vision.
Potential use-cases
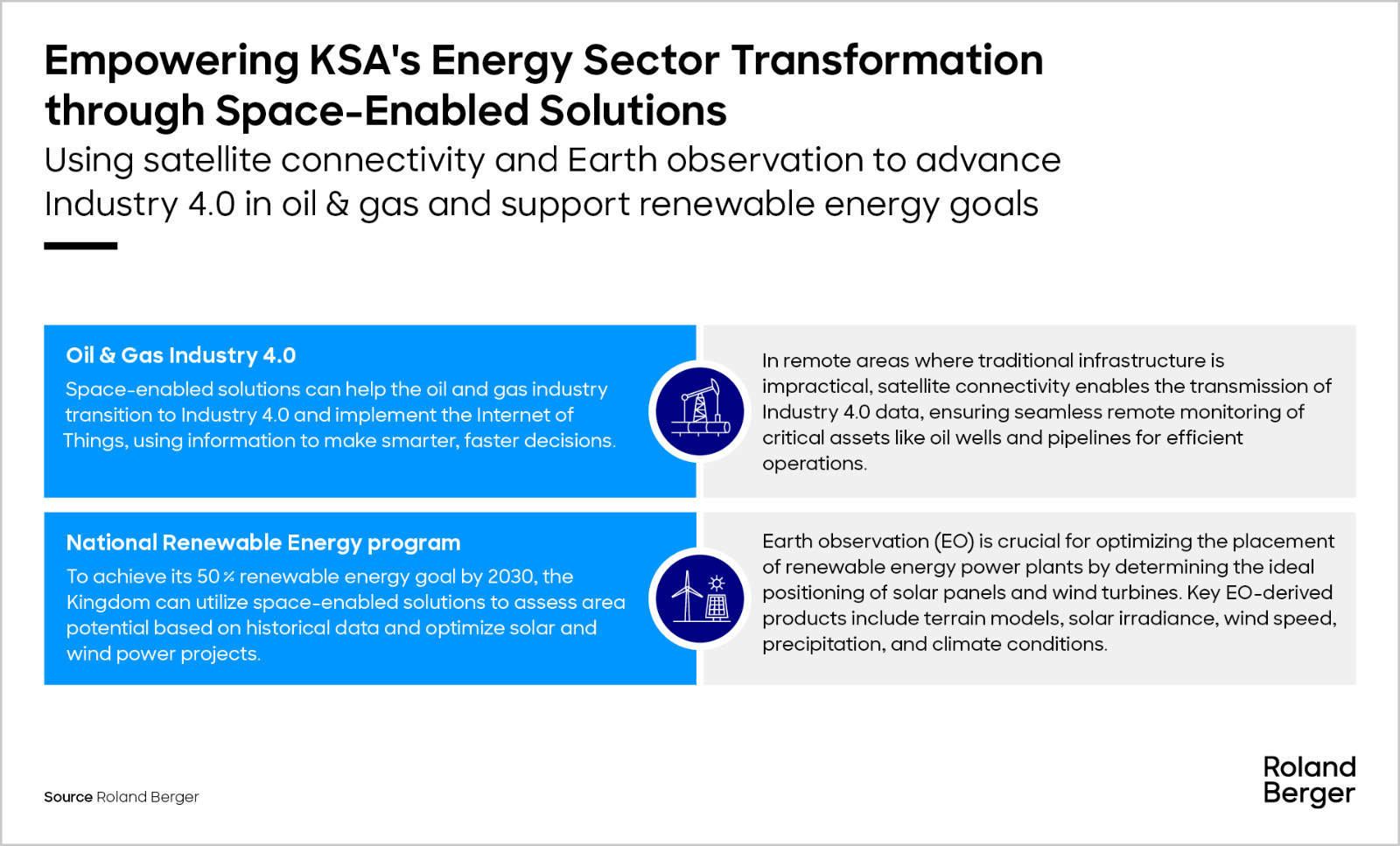
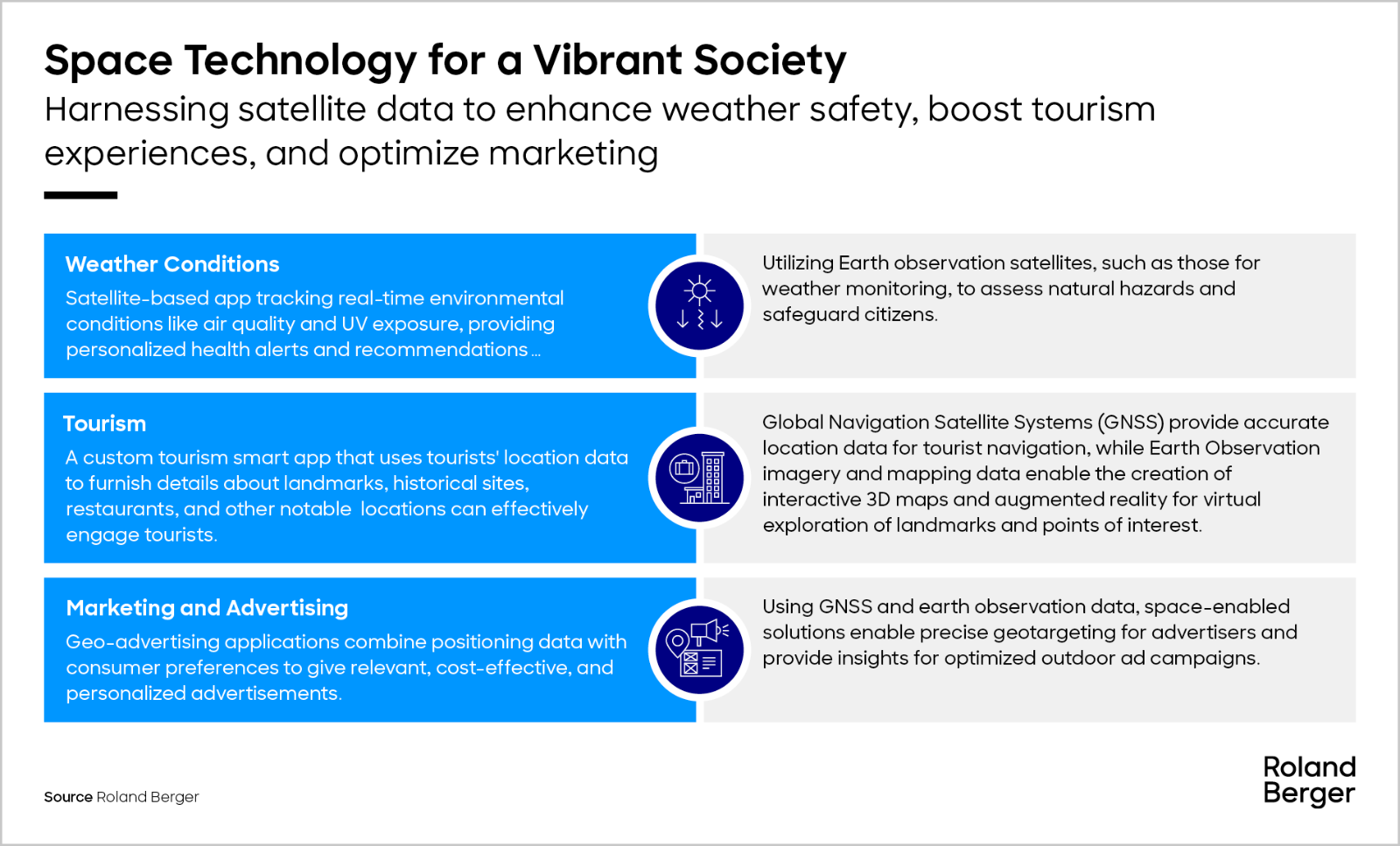
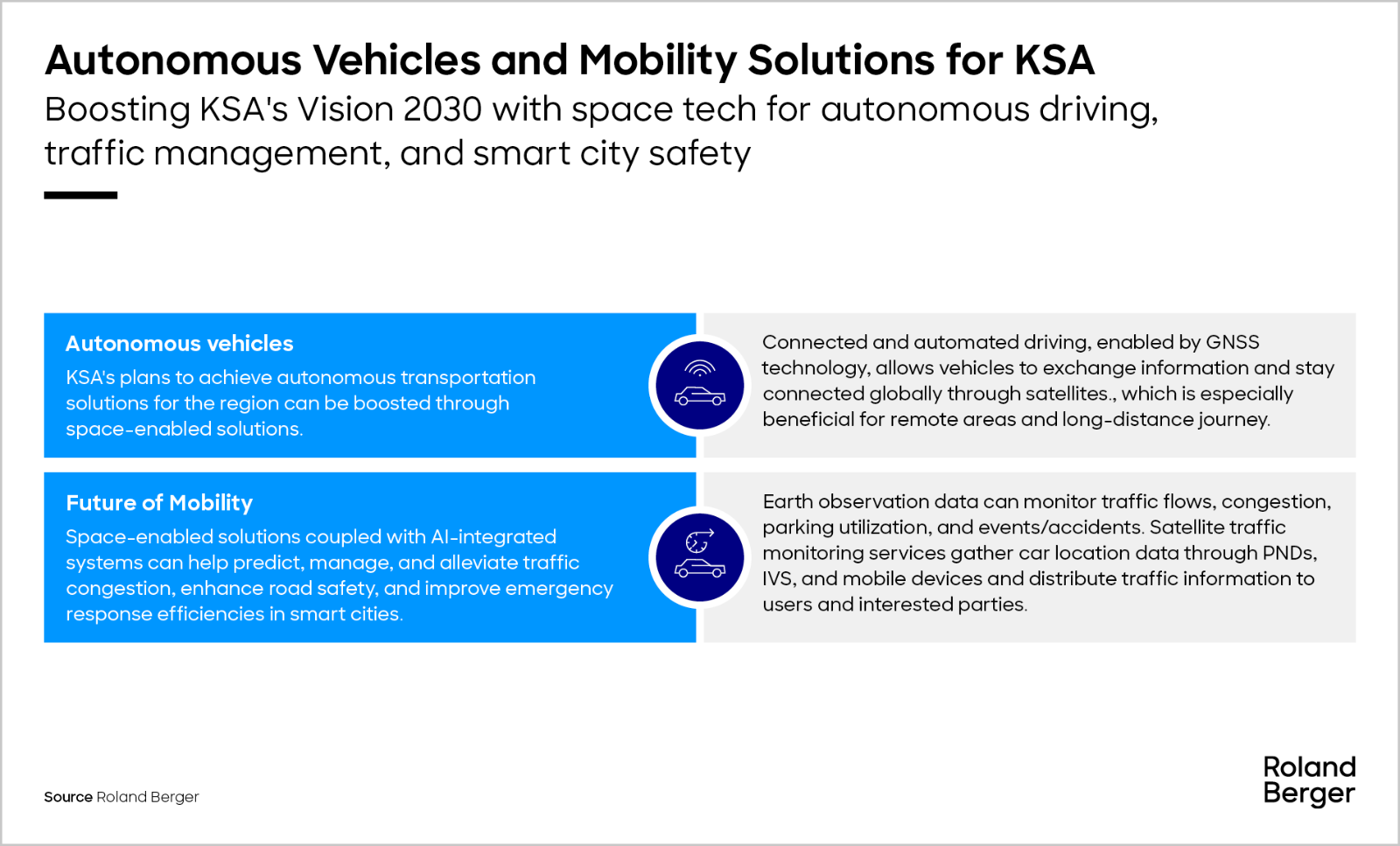
Out of the 17 sectors analyzed for global growth in space-enabled solutions, we have conducted an in-depth examination of four key sectors essential for KSA’s development goals to explore potential use cases.
How to make it happen?
In propelling KSA towards a future integrated with space technologies, Roland Berger recommends the following next steps:
- Shaping the ecosystem
Assessing the potential for success in the space sector, involving and rallying key stakeholders in KSA, including governmental bodies, private enterprises, academic institutions, and research centers. - Ensuring a supportive environment
Establishing a proactive and conducive regulatory framework, making investments, and developing the infrastructure needed to accommodate new space markets and cultivate growth. - Driving initiatives
Implementing pilot projects and initiatives aimed at advancing the Kingdom's space strategy - Commercializing solutions
Transforming space-related innovations into marketable products and services, driving economic growth
Roland Berger has developed a comprehensive stakeholder framework and identified key success indicators tailored to each ecosystem participant.
KSA Space Agencies: Take the initiative to develop partnerships with stakeholders, establish collaboration frameworks, and create space sector innovation and entrepreneurship platforms.
- Ministries: Implement policies, regulations, and infrastructure that encourage the adoption of space technologies, engage businesses, and enable innovation. They should also streamline administrative processes and provide financial incentives and support mechanisms for startups and SMEs.
- Regional Space players: Focus on fostering a culture of innovation and agility, embracing emerging space technologies, and developing space-enabled solutions tailored to regional needs.
- End-users: They are pivotal in driving the demand for space-enabled solutions by sharing their business challenges and real-world requirements. Their insights and perspectives guide the development of market-oriented solutions.
- Academia and research institutions: develop a space know-how curriculum that aligns with industry needs, integrate cutting-edge research and practical training, and provide students with hands-on learning experiences and research opportunities.
- International space agencies: encourage international cooperation is essential for KSA to advance its capabilities and contribute to global scientific endeavors. KSA should identify areas of mutual interest and offer incentives for collaboration.
- International space players: develop strategic partnerships with government agencies, research institutions, and private companies to accelerate the development and deployment of space technologies and solutions.
- Defense players: leverage defense capabilities and support dual-use applications by identifying synergies between defense and space technologies and contributing to advancing space capabilities while safeguarding national security interests.
- Investors: actively seek investment opportunities in startups and emerging companies that offer space-enabled solutions. They should prioritize sustainable investment practices that align with national goals and contribute to the expansion and diversification of the space ecosystem.
By harnessing the vast potential of the space sector, KSA can fortify its leadership across pivotal areas of the economy. Much like digitalization, space serves as a powerful catalyst, possessing the capacity to exponentially amplify the nation's industrial prowess and competitive edge.
Recognizing this transformative potential, Roland Berger believes that constructing an inclusive space ecosystem is indispensable for realizing KSA's ambitions in the sector and aligning with Vision 2030. KSA can adeptly navigate challenges and leverage space solutions to propel innovation, spur economic growth, and achieve strategic advancements.