EV sales are strong, but Switzerland must address its insufficient fast-charging infrastructure. Discover more in the Roland Berger EV Charging Index 2024.


Swiss Economic Outlook 2025
By Matthias Hanke and Sven Siepen
Swiss economy shows modest growth amid mixed sectoral performance
Switzerland's economy continues to demonstrate remarkable resilience in the face of mounting global uncertainties, recording a sports-event adjusted growth of 1.0% in 2024. With easing inflation, lower interest rates, and a boost in consumer confidence, prospects for a stronger expansion in 2025 are on the horizon. Yet, rising geopolitical tensions and a shift towards protectionism cast a shadow over these forecasts.

-
Throughout the first three quarters of 2024, Switzerland’s GDP experienced moderate growth, with a mixed performance across sectors. The chemicals and pharmaceuticals sector drove the slightly above-average growth in manufacturing, while other manufacturing segments experienced a slight decline in value added, reflecting the subdued momentum in global manufacturing. Exports also made a significant contribution to GDP growth, supported by a robust increase in pharma exports. In contrast, private consumption grew at a below-average pace, and investment registered a decline. Overall, sport-event adjusted growth in 2024 is expected at around 1.0%.
"Throughout the first three quarters of 2024, Switzerland’s GDP experienced moderate growth, with a mixed performance across sectors. In Q3 2024, Swiss GDP growth decelerated due to weak manufacturing and export declines. "
Supported by the strong Franc, inflation rates are normalizing to pre-Covid levels
In December 2024, inflation reached 0.6% year-over-year, marking another slight decrease compared to November. [SG1] Core inflation, which excludes volatile items like energy and food, was stable compared to November. Domestic goods prices rose by 1.9% year-over-year, contrasting with a 1.5% decline in imported goods prices.
The recent easing of inflation is largely attributed to lower prices for international package holidays, medicines, and several types of vegetables. In contrast, prices for supplementary accommodation and hotels increased. For the entire year 2024, inflation averaged at 1.1%. For 2025, it is expected to further decline.
"Switzerland’s economy proves its resilience once again—exports surge, inflation stays low, and innovation keeps us ahead. Even as global challenges mount, Swiss stability remains our greatest asset."
The Swiss National Bank continues to ease its monetary policy. The SNB key interest rate is significantly lower compared to the Fed's and ECB's main rates
In December 2024, the Swiss National Bank (SNB) has lowered its key interest rate for the fourth time in a row. Following the latest reduction of 0.5 percentage points, the interest rate now stands at 0.5%. The SNB had already cut the interest rate by 0.25 percentage points in March, June, and September. The decision in March in particular caused a stir, as the SNB was one of the first major central banks to cut interest rates. The SNB emphasized that it is still prepared to become active on the foreign exchange market if necessary to stabilize the exchange rate.
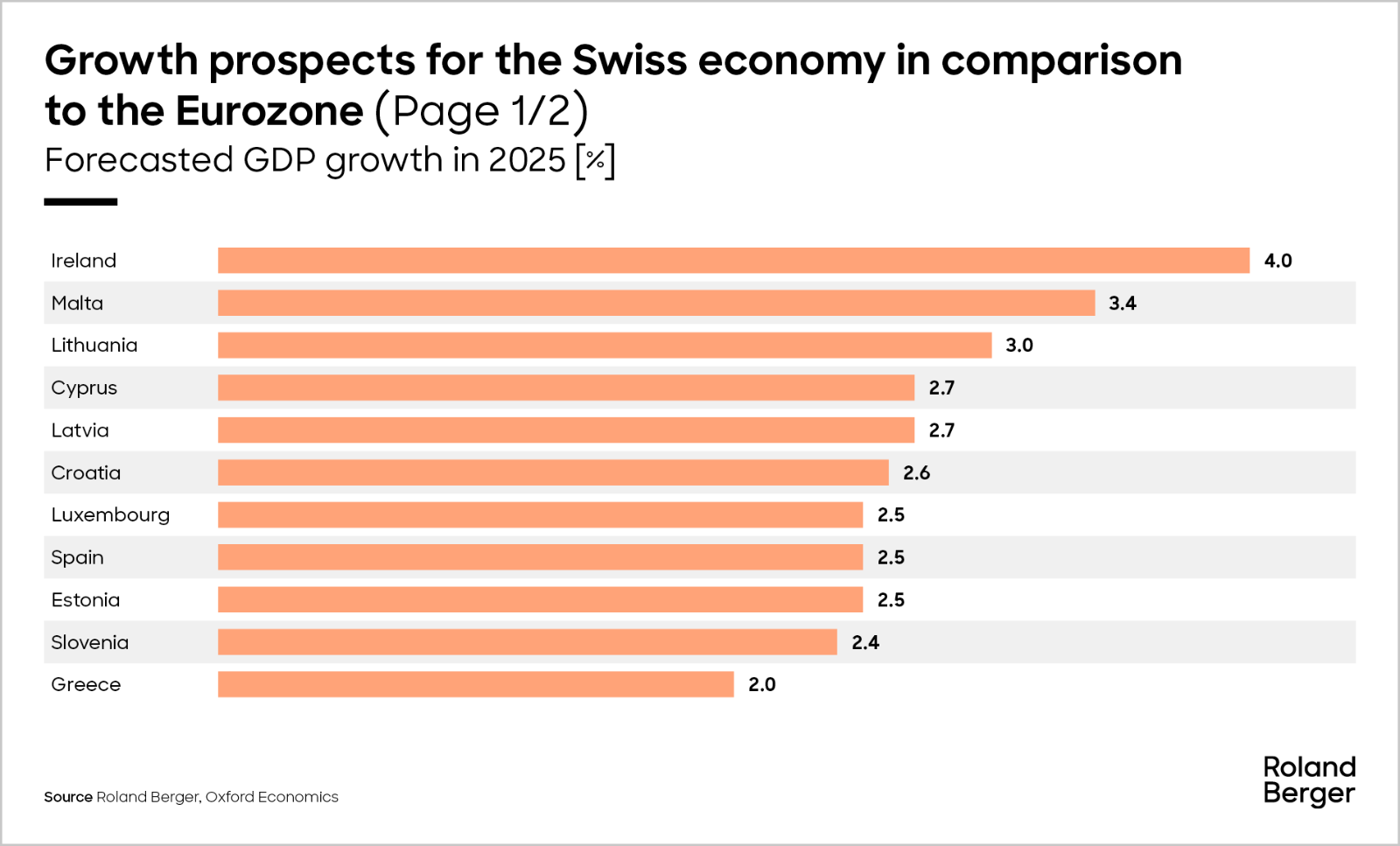
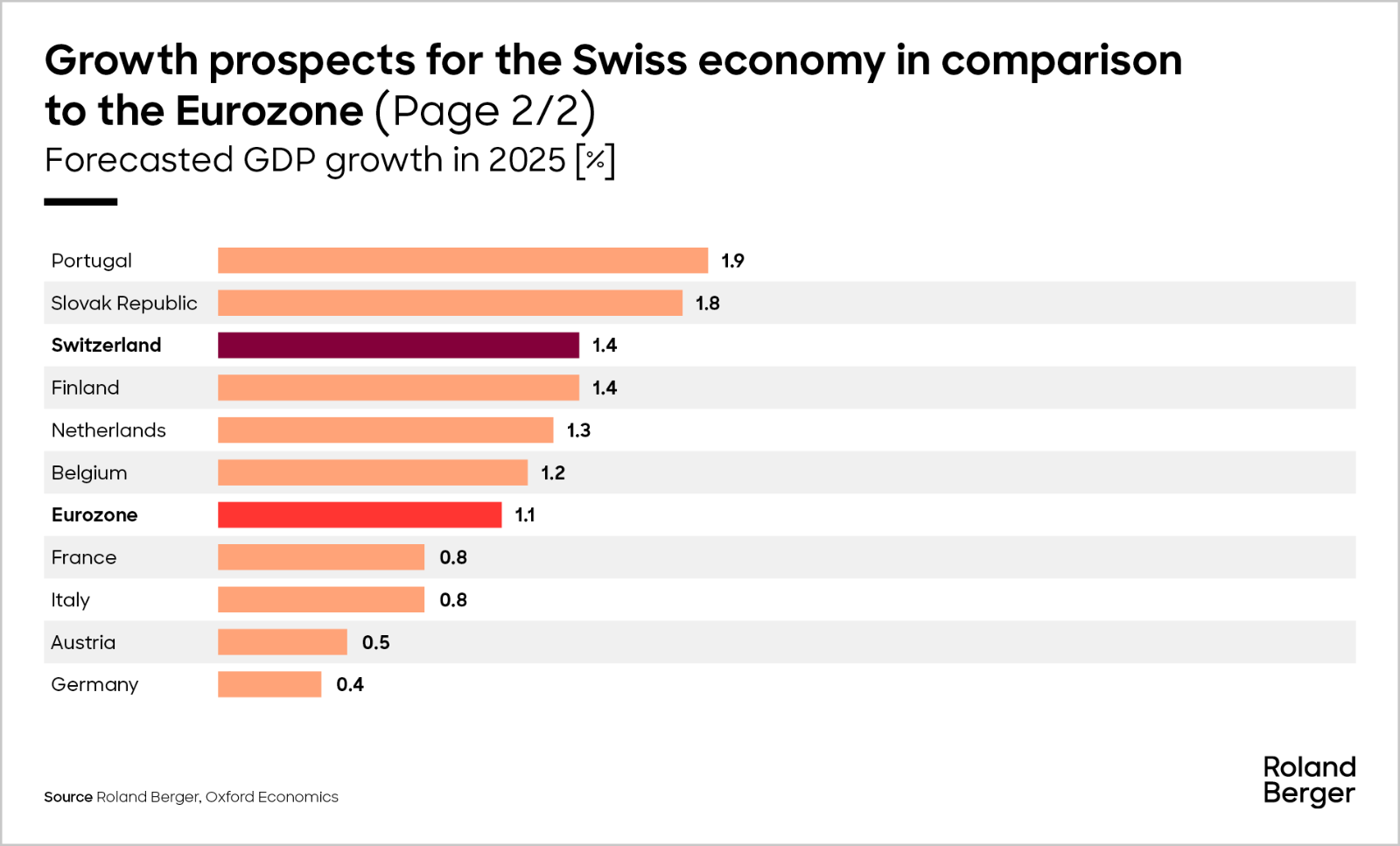
Our Economic outlook for 2025: Switzerland is growing stronger than the Eurozone average. Growth will likely moderate in 2025 as domestic conditions brighten but external risks loom
Propelled by easing inflation and lower interest rates, consumer spending is set to rise and investment is expected to rebound in 2025. However, mounting geopolitical uncertainty and a shift towards protectionism are likely to bolster the Swiss franc further - a development that could dampen export growth. In summary, domestic conditions are set to improve, while external risks are likely to intensify. Growth is expected to edge up to sport-event adjused 1.4% in 2025, slightly higher than in 2024. This positions Switzerland ahead of the eurozone average, as economic heavyweights like France and Germany continue to drag down the bloc's performance with their lackluster development.
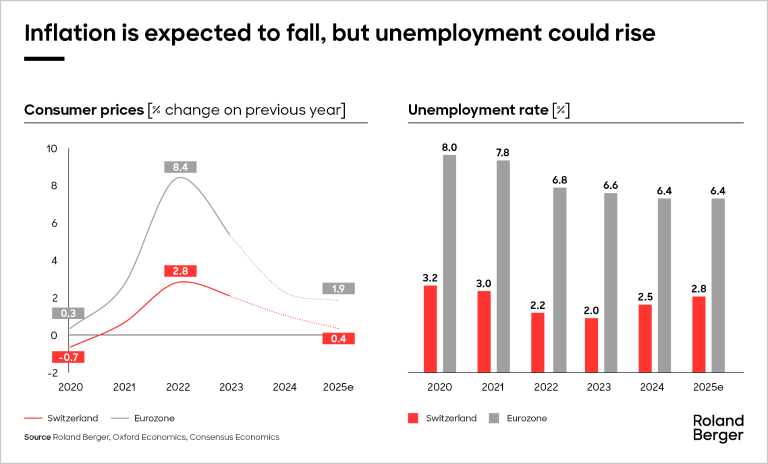
Swiss economic crossroads: Inflation down, job concerns rise
Falling inflation rates in Switzerland and the Eurozone indicate that price stability is returning to the continent. As both the SNB and ECB have started cutting rates, easing inflation should provide more space for future cuts. However, this space should be considerably larger for the SNB as Switzerland’s economy is growing faster and inflation is lower. Low inflation and upward pressure on unemployment has led to the SNB cutting its policy rate by 0.5 percentage point to 0.5% in December 2024.
While inflation is expected to fall, unemployment could increase in the coming year and is already above pre-pandemic levels in Switzerland. Due to the slight slowdown in the Swiss economy, we expect a minor increase in unemployment.
Register now to access the full economic outlook, 'The Swiss Economy in 2025,' and delve into how Switzerland's economy is set to maintain solid growth despite mounting external challenges. Furthermore, you get regular news and updates directly in your inbox.



![Growth of Gross Domestic Product 2019-2024 [%]](https://img.rolandberger.com/content_assets/content_images/captions/Roland_Berger_24_2660_Swiss_economic_outlook_RBI_GT01_image_caption_none.png)
![Inflation rate 2019-2024 [%]](https://img.rolandberger.com/content_assets/content_images/captions/Roland_Berger_24_2660_Swiss_economic_outlook_RBI_GT02_image_caption_none.png)