The Future of Dentistry is Digital
How digital innovation is reshaping administrative and clinical processes
Within dental care, several fundamental and mutually reinforcing trends drive deep structural changes, and embracing advanced digital solutions will become imperative to stay ahead of the competition. Consolidation into dental chains has picked up speed, while simultaneously, technological advancements, low-cost alternatives, a lack of qualified personnel, changing patient preferences and dental school curricula, as well as new treatment standards are further accelerating the adoption of digital solutions. These advanced solutions will eventually cover the entire dental workflow, delivering quantifiable benefits for dentists, technicians and – most importantly – patients. Ultimately, those clinics that are excelling at digitalization will gain considerable advantages in terms of outcome quality, as well as cost and time savings.
"Unlike labs, dental clinics have been much slower at adopting digital solutions. Sales of intra-oral scanners, which produce a digital impression, have been growing recently, yet very few dentists are using them – currently around 10-20%. It would be fair to say that this technology is still in the early adopter phase."
Dental care is ripe to go digital
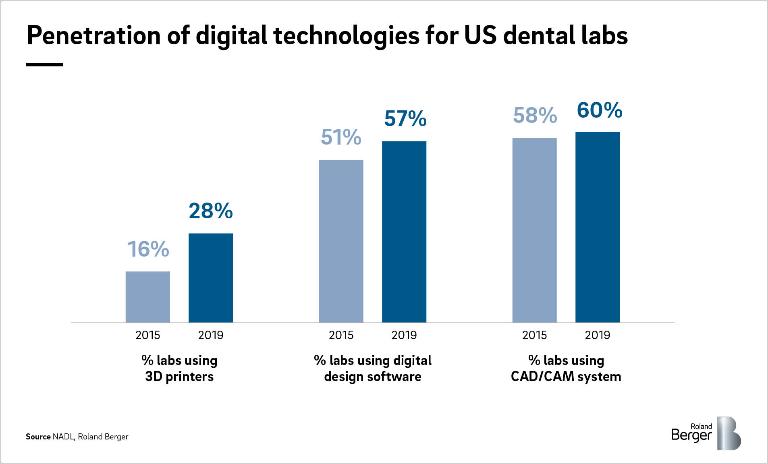
For years, dentists, nurses and dental technicians in small laboratories have been delivering treatment and prosthetics relying mainly on analog tools and manual ways of working. While early digital systems such as CAD/CAM were introduced as far back as the 1980s and quickly adopted by larger laboratories due to their high volumes and standardized processes, still less than 20% of dental clinics are usingCAD/CAM systems across the US and Europe (2018). In addition, the exchange of information and workflows between dentists and laboratories are still largely analog and AI-supported imaging solutions common in medical fields such as radiology or fertility have not yet seen their breakthrough in dentistry.
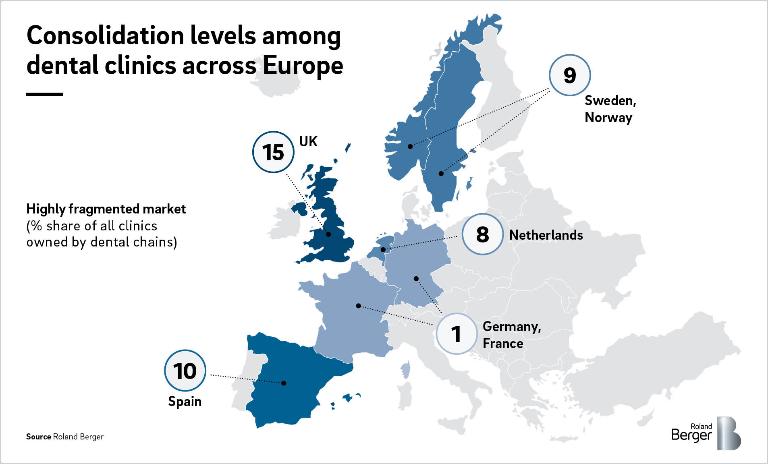
Dentists' reluctance to adopt digital innovations in the past had both economic and structural reasons: Other parts of the healthcare system have been experiencing consolidation for quite some time, yet the dental care market has traditionally been – and still is – highly fragmented. In Europe, private chains make up 15% of the total number of clinics in the UK, 8-10% in the Nordics and Spain, 8% in the Netherlands, while in Germany and France this share drops to below 1% of the total dental care market.
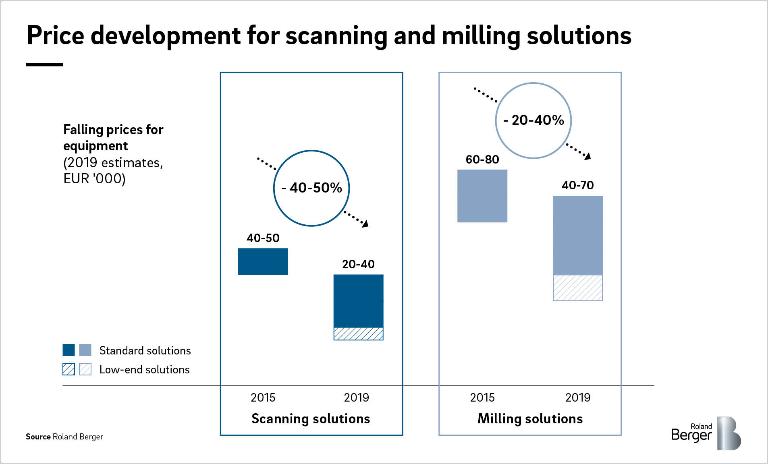
This fragmentation has limited individual clinics' ability to invest in advanced equipment, given that starting up a dental clinic involves significant upfront investments of EUR 400-900 k in facilities, basic equipment and consumables, as well as efforts to hire mid-level employees such as hygienists and nurses. Historically,the price of advanced digital solutions such as scanning and milling devices has been too high and utilization levels too uncertain to pay off for most individual practice owners, thereby giving them limited incentives to invest. Moreover, individual practice owners usually exhibit a lower level of professionalization in administration and documentation. However, these barriers and reservations to change are slowly starting to give way and dentists are beginning to embrace digital solutions in their workplace.
Seven fundamental trends drive the adoption of digital innovations
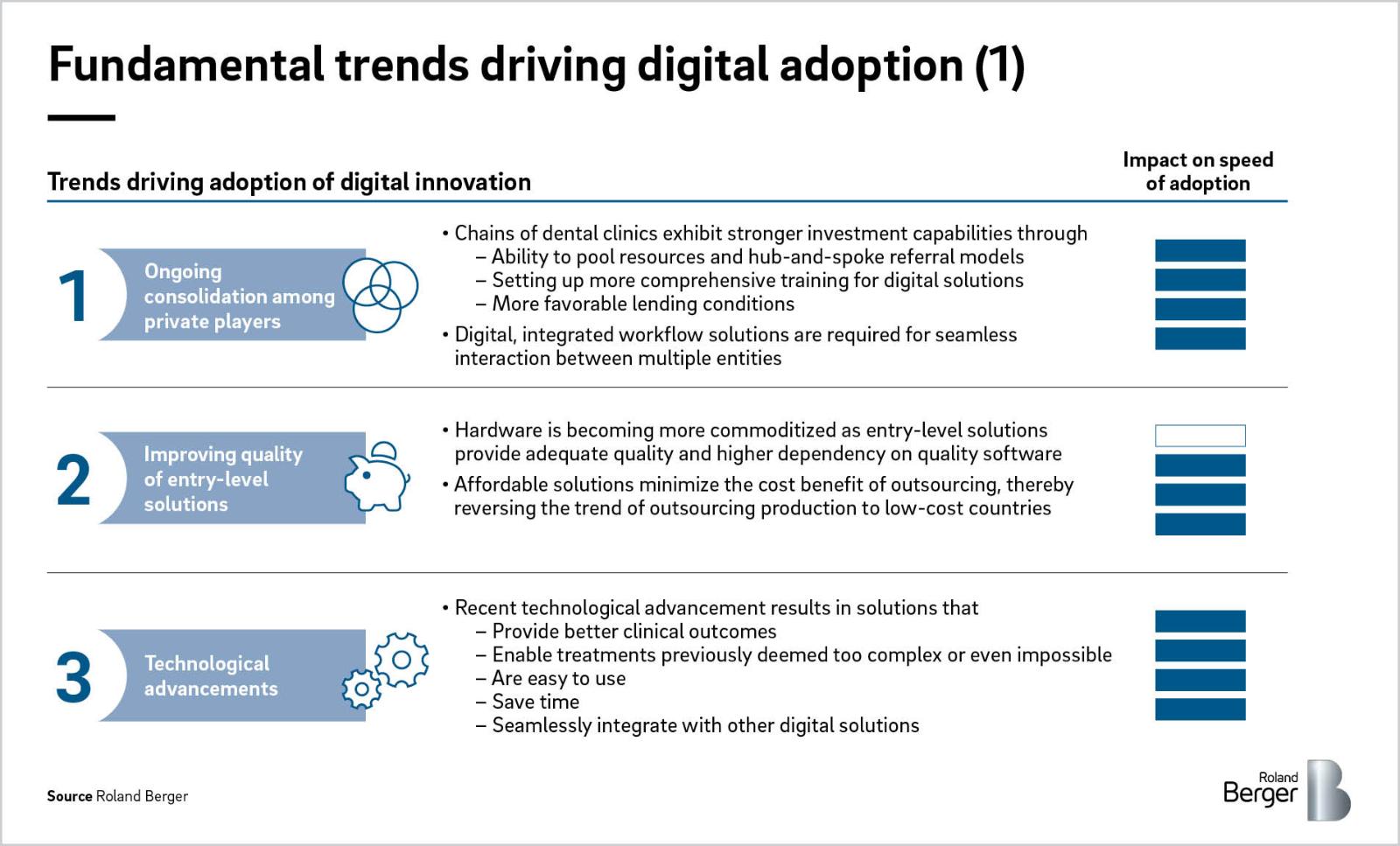
Over the course of the next 5-10 years, the adoption of digital innovations in dental care will be driven by seven fundamental, mutually reinforcing trends.
1. Ongoing consolidation among private players
Among dental laboratories, the formation of chains and resulting consolidation in the EU that began 10-15 years ago, as well as low-cost offerings from countries like China, have fueled investments in digital solutions such as CAD/CAM, necessary to stay competitive. This has dramatically changed the economics of running a dental laboratory.
More recently, a similar consolidation trend has been observed among dental clinics, with previously regional dental chains expanding throughout the EU. Fueled by private equity investments, chains increasingly take a more long-term strategic and commercial approach to dental care. Chains' ability to access financing, specialize operations and train personnel are key drivers behind the accelerating adoption of digital technologies.
Additionally, as clinics integrate further along the value chain by opening or acquiring their own laboratories, they will intensify their efforts to digitalize and integrate workflows to improve speed and accuracy of communication across multiple entities while reducing costs associated with administrative work. Through our involvement in recent transactions, we have seen the importance of strong IT and digital capabilities reflected in the scope for diligencing and delivering the equity story.
2. Improving quality of entry-level solutions
During the previous decades, production of dental prosthetics and appliances has been frequently outsourced to low-cost countries. Yet with recent digital innovations,even medium-sized labs and dental clinics are able to achieve lower costs and adequate quality by producing in-house on affordable entry-level hardware paired with high-quality software. In addition, the current COVID-19 pandemic has tremendously affected the supply and transport of dental products into and within the EU, and we see this as a further accelerator for the adoption of in-house CAD/CAM systems and as an inflection point for reversing previous outsourcing decisions.
Strategic alliances between dental equipment and technology companies allow for deeper integration with other software via APIs and convey the ability to customize digital workflows to fit users' needs. In support of this trend, many previously closed solutions such as CAD/CAM systems are opening up to allow users to choose specific software and hardware more freely.
3. Technological advancements
Over the past 5-10 years, we have seen remarkable advancements in computer technology and prosthetics production, disrupting the entire dentistry workflow –from the way patients are diagnosed to the design of prosthetics to how surgeries are planned and conducted and how patient data is exchanged and stored. Digital solutions are not just becoming more accessible, they also consistently provide better and controllable outcomes while drastically reduce time requirements. Treatments which were previously too complex or even impossible to achieve are now part of the daily routine. Together with more comfortable and individualized treatments, overall patient satisfaction will increase significantly. Considering these benefits, previously unreasonable upfront investments in advanced solutions become a viable alternative to analog methods or outsourcing of production.
Other major, long-term technological advancements are AI and machine learning solutions. AI is expected to play an increasingly important role in the automation of design and manufacturing of complicated dental applications and restorations, while these technologies will continue to improve their image analysis capabilities.
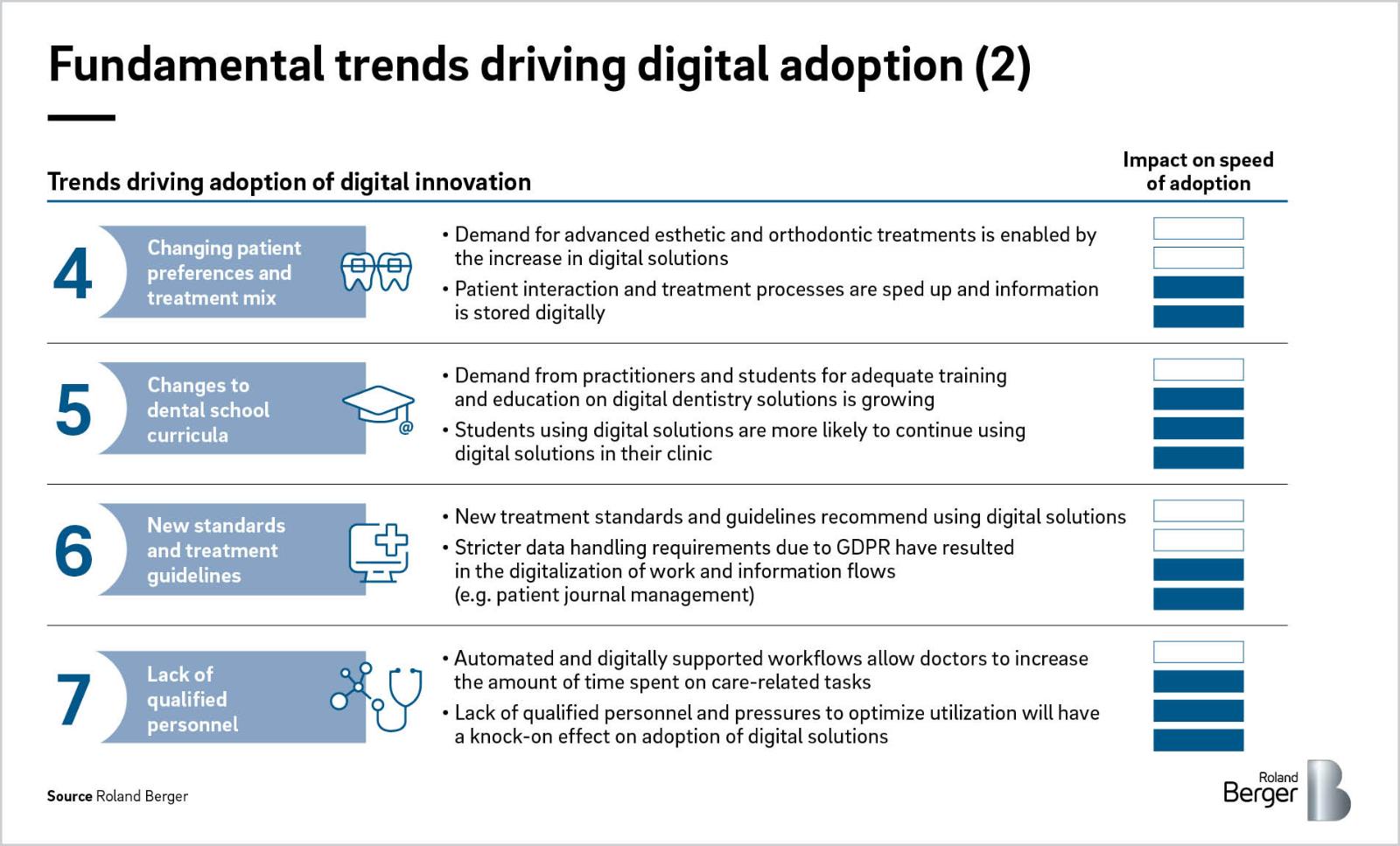
4. Changing patient preferences and treatment mix
Dentists have for a long time benefitted from loyal patients, yet as transparency regarding price and treatment quality increases and possibilities of advanced aesthetic and orthodontic treatments expand, demand from patients is following accordingly. Whereas it was common to visit the dentist for multiple session stretching over days or weeks to receive implants, dentists are now able to diagnose, plan and treat their patients in one or two sessions due to digital imaging and planning solutions enabling seamless information transfer. Digital workflows are further made possible by patients increasing acceptance of – and trust in – digital information storage.
5. Changes to dental school curricula
Historically, teaching institutions only reluctantly included education on digital solutions such as CAD/CAM in their curricula. This reluctance has given way in recent years driven by studies proving superior clinical outcomes with digital solutions and growing demand from practitioners for students with prior experience in using complex hardware and software. Also, students themselves are becoming more open towards digitalizing significant parts of their workplace due to overwhelmingly positive experiences from testing digital solutions during their studies.
Going forward, digital knowledge-sharing tools will further accelerate the usage of software among students, and proactive educational cooperations with dental technology companies will allow schools to obtain relevant qualifications and expertise.
6. New standards and treatment guidelines
In recent years, stricter treatment guidelines recommend employing digital solutions to ensure outcome or production quality. When it comes to patient management,stricter documentation and administrative requirements in line with GDPR push dentists and laboratories towards digitalizing entire work and information flows to ensure compliance. One thing is clear: As technology moves forward, so will the rules and regulations for digital dentistry. This will have implications for both dental companies and practitioners as approval and validation processes for production and equipment usage become stricter and adherence is no longer feasible using solely analog processes.
7. Lack of qualified personnel
As with many other healthcare specializations, qualified dentists and nurses are in short supply and demographic developments will amplify this trend in the coming years, as 30% of all dentists in Europe are over 55 years old. As a result, adoption of digital technologies will compensate for fewer numbers of dentists by bringing increases in productivity and efficiency. As older dentists retire and younger dentists enter the workforce, an additional knock-on effect will further boost the uptake of digital solutions.
As an example of how digital solutions can help improve efficiency and bridge personnel shortages, one only needs to look at how a shortage in radiologists has been tackled in the UK: A shortage of local radiologists has led to an outsourcing of image analysis via digital solutions. Images are sent to radiologists living in countries in entirely different time zones (e.g. Australia), images are analyzed over night with the support of analysis software, and results from the analyses are provided to patients in the UK the day after, thereby both speeding up the analysis and compensating for a lack of local radiologists.
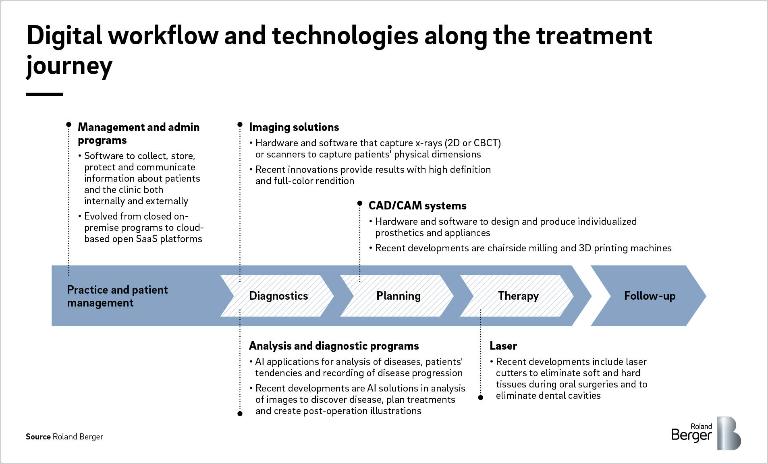
Digital technologies will cover the entire dental workflow
So the key question now is: How can dental players accelerate digital adoption and leverage the potential of advanced digital solutions to ensure comprehensive care and support throughout all interfaces of the care process? By fully embracing digital technologies, clinics and laboratories have the possibility to digitally replicate their entire operations and ensure a standardized exchange of information along the entire dental workflow from diagnostics to therapy.
CAD/CAM
CAD/CAM systems have quickly been adopted by large dental labs, with penetration levels among labs in Europe and the US reaching 60% in 2019. Differences between different lab sizes are striking: In the US, and similarly in Europe, only 45% of small labs (<9 FTE) use a CAD/CAM system, whereas 98% of large labs (>25 FTE) either own or lease such a system.
Recent developments in 3D printing have expanded the technology's use cases to include dental models, orthodontic appliances, mouth guards and appliances for guided implant surgery, as well as the production of removable and fixed prosthetics.
Another major development is the gradual shift from laboratories to chairside CAD/CAM systems. The technology has matured rapidly, and larger dental practices have started to work frequently with their own chairside systems. Technological advancements and the availability of viable low-cost hardware/software alternatives are further accelerating the adoption of chairside CAD/CAM systems even among smaller dental clinics.
Imaging solutions
Since the introduction of intra-oral scanners, the technology has improved remarkably.The most recent versions, which are smaller in size, offer quick scanning and instant visualization and have the ability to navigate seamlessly in the oral cavity. For the patient, these benefits translate into higher comfort and better communication, while dentists benefit from time savings of up to 60% and a reduction in scanning errors. Given that adoption among dentists is still low, we foresee significant growth potential in the years to come, with 3D imaging devices overtaking sales of traditional 2D devices and adoption by a much wider group of dentists.
Laser tools
Dental lasers have been used on a small scale since the 1990s, proving excellent efficiency in procedures like crown lengthening and wisdom tooth extraction but also in treating dental cavities. In recent years, the adoption of dental lasers has increased significantly, driven by the development of lasers with smaller hand-pieces and more precise, ergonomic and effective cutting features.
Management programs
Digital management programs replace analog records in collecting, storing and sharing patients' medical journals with care providers. During the last decade, programs evolved from being closed, on-premise systems to cloud-based, open platform SaaS solutions. Numerous add-ons, modules and apps allow for API integration and open up possibilities such as data encryption and authorization barriers, data analysis, patient flow management and patient communication (including follow-up).
In the coming years, we expect to see even greater integration and personalization, as well as easier access to personal data via mobile apps. At the same time, communication and secure data sharing between different stakeholders will be enhanced, covering dentists, dental technicians and also health authorities and insurance partners.
Analysis and diagnostics programs
Due to the explosive progress in AI and machine learning applications, analysis programs can now be used to analyze large and complex data such as X-ray images to detect caries, osteoporosis and orthodontic deformities, among other things. Given that startups focused on these types of applications have received both attention from dentists and a steady flow of funding from venture capitalists and medical technology companies, we expect massmarket adoption of intelligent applications to take off during the coming years.
Adoption of digital solutions provide quantifiable benefits
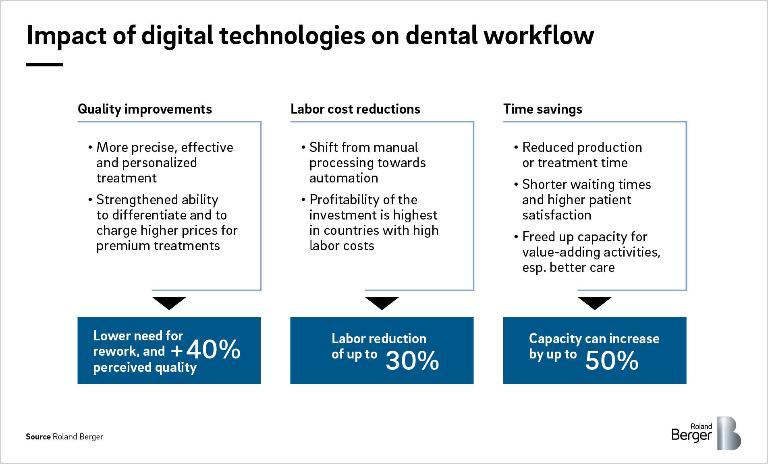
Digital dentistry is not just a buzzword – digitalization of dental care workflows provides quantifiable benefits in terms of quality, time savings and labor cost reductions.
Looking at premium dental chains and laboratories, digital solutions are much more common place and prominently communicated to convey a sense of quality and a high level of innovation. Ultimately, comfortable and quality treatments, as well as more consistent and controllable production outcomes will allow both laboratories and dentists to differentiate themselves in a demanding market towards both employees and patients – and command a premium for their services.
Digitalizing and automating manual tasks can reduce labor costs for traditional dental labs by up to 30%. In terms of efficiency, digital solutions allow for the significant reduction of production and treatment time, and technologies such as CAD/CAM systems can free up capacity amounting to as much as 50%. Similar time and cost savings can be achieved for administrative and diagnostic tasks, freeing up time for better dentist-patient communication and involvement of patients in their treatment journey – one of the most important factors in earning patient loyalty. In addition, the lower administrative burden also increases the employer attractiveness of digitally advanced dental clinics over the more traditional competitors.
There is no question that digital technologies are rapidly gaining traction. In the coming years, we expect dentists not only to adopt already mature technologies but to engage with emerging intelligent solutions. Solutions that will further disrupt the dental care market by delivering additional benefits for dentists, technicians and – most importantly – patients. Now the real question is: Who will seize the opportunity and react in time to ensure they come out on top?
Credentials
Over the years, we have worked with a variety of dental players, developing proprietary insights and tools to support companies on a range of topics – from digitalization and growth strategies to value creation plans, performance improvement initiatives and due diligence support.
We will be happy to discuss the implications and benefits of digitalization for your organization, as well as potential investment opportunities within the dental and broader life sciences landscape.
Please don't hesitate to get in touch with us.